Housing: Turret, - Resolution: 4MP, - Lens: 2.8mm Fixed, - Night Vision: Full Time Color, Infrared / IR, LED, Starlight, - WDR: True WDR, - Water

HNC3IV349TM-IRASPV || Diamond, IPC, 4MP, Turret, 2.8mm Fixed
Housing: Turret, - Resolution: 4MP, - Lens Category: 2.8mm Fixed, - Night Vision: Infrared / IR, Starlight, - WDR: True WDR, - Water Resistance

HNC3IV341TM-IRAS/28 || Diamond, IPC, 4MP, Turret, 2.8mm Fixed
Learn how to use the k-Nearest Neighbor (k-NN) classifier for image classification and discover how to use k-NN to recognize animals (dogs & cats) in images
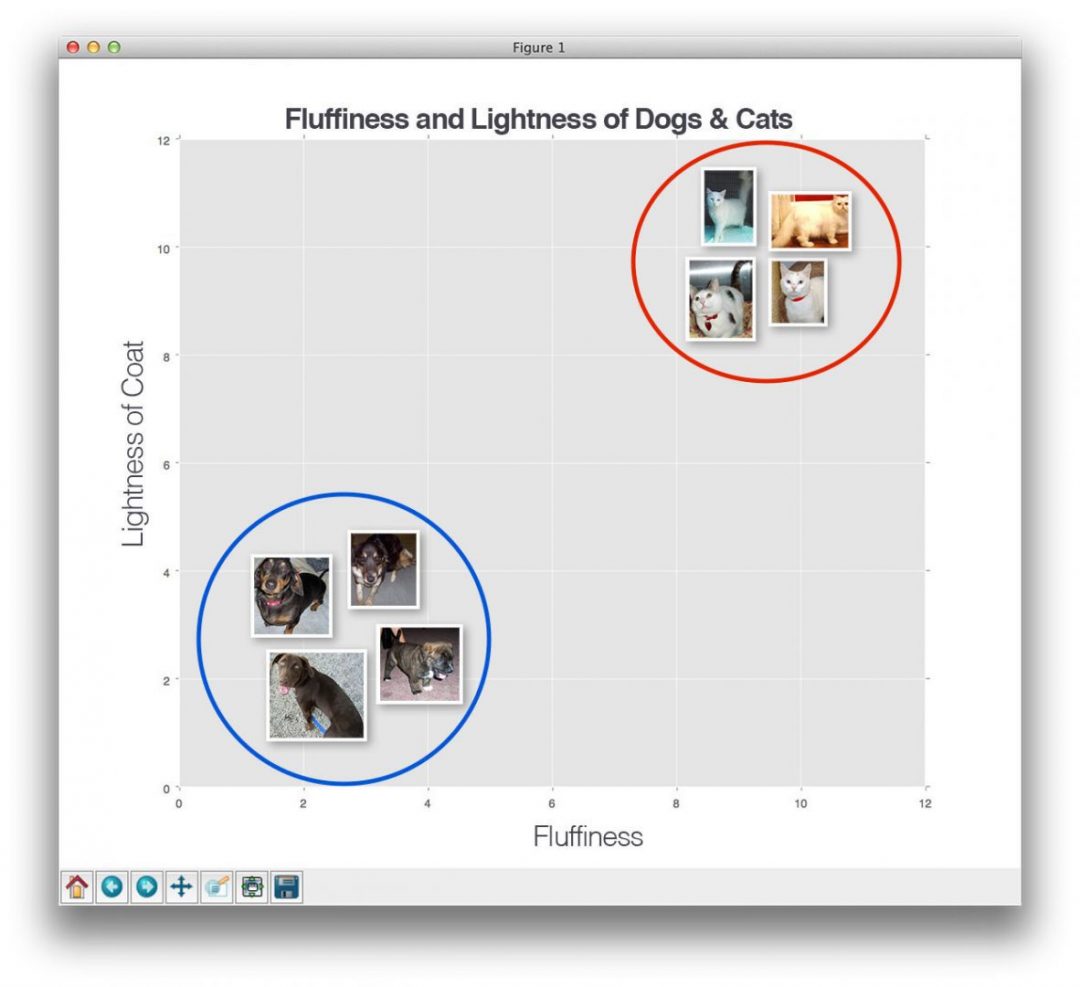
k-NN classifier for image classification - PyImageSearch
CS231n/assignment1/knn.ipynb at master · jariasf/CS231n · GitHub
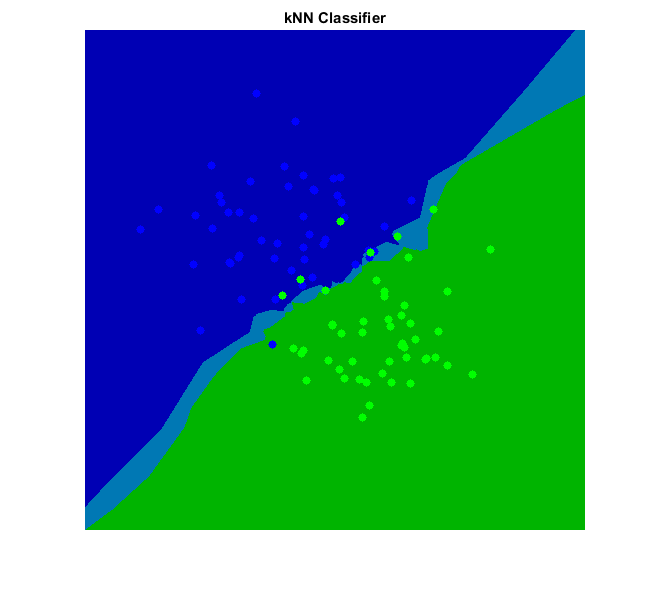
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)
CMPE-255-Fa18-Data_Mining_updated/lsh.py at master · hemangbehl
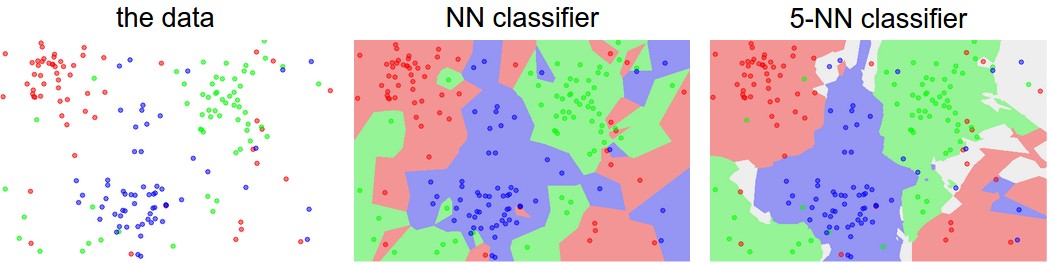
CS231n Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition
Running shoes Nike AIR ZOOM STRUCTURE 21
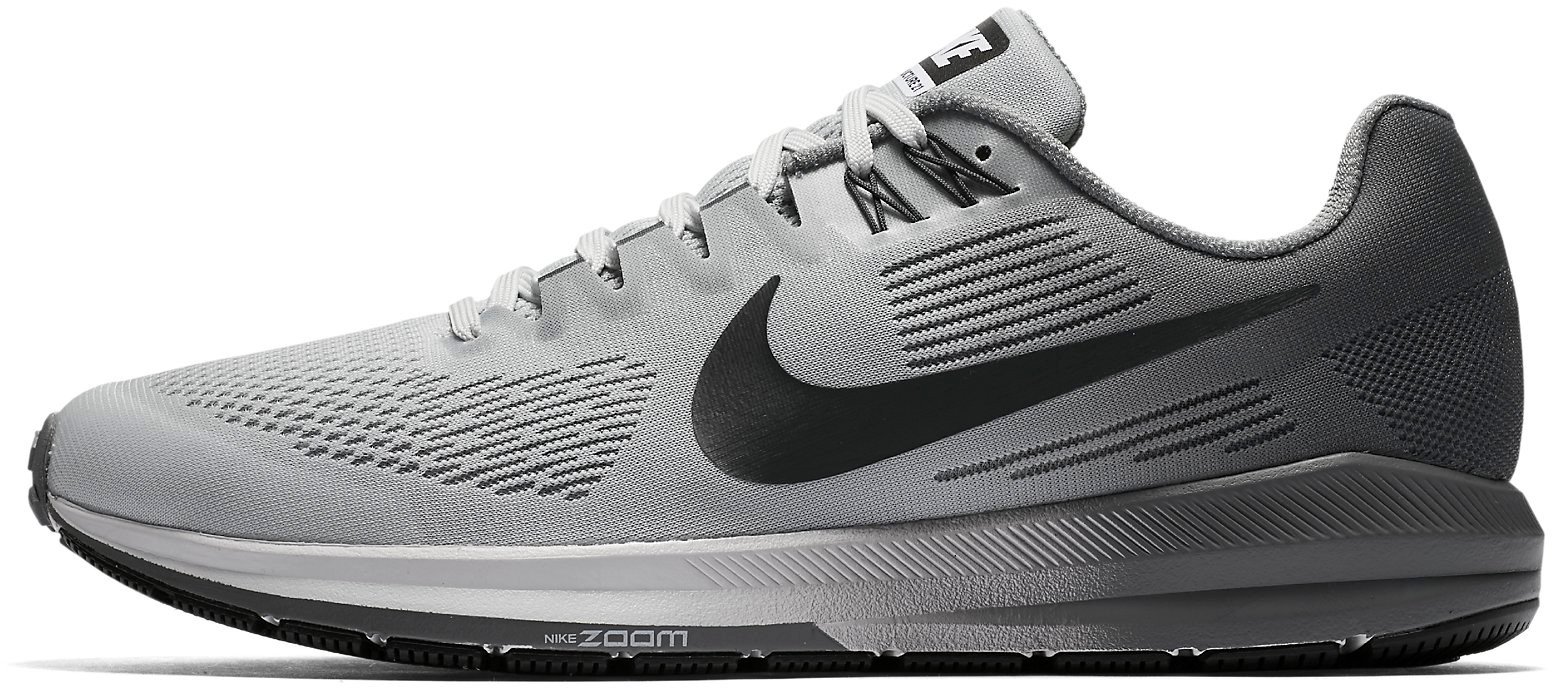

Running shoes Nike AIR ZOOM STRUCTURE 21
Optical and thermal remote sensing data have been an important tool in geological exploration for certain deposit types. However, the present economic and technological advances demand the adaptation of the remote sensing data and image processing techniques to the exploration of other raw materials like lithium (Li). A bibliometric analysis, using a systematic review approach, was made to understand the recent interest in the application of remote sensing methods in Li exploration. A review of the application studies and developments in this field was also made. Throughout the paper, the addressed topics include: (i) achievements made in Li exploration using remote sensing methods; (ii) the main weaknesses of the approaches; (iii) how to overcome these difficulties; and (iv) the expected research perspectives. We expect that the number of studies concerning this topic will increase in the near future and that remote sensing will become an integrated and fundamental tool in Li exploration.
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text
The recent rise of deep learning (DL) and its promising capabilities in capturing non-explicit detail from large datasets have attracted substantial research attention in the field of medical image processing. DL provides grounds for technological development of computer-aided diagnosis and segmentation in radiology and radiation oncology. Amongst the anatomical locations where recent auto-segmentation algorithms have been employed, the pelvis remains one of the most challenging due to large intra- and inter-patient soft-tissue variabilities. This review provides a comprehensive, non-systematic and clinically-oriented overview of 74 DL-based segmentation studies, published between January 2016 and December 2020, for bladder, prostate, cervical and rectal cancers on computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), highlighting the key findings, challenges and limitations.
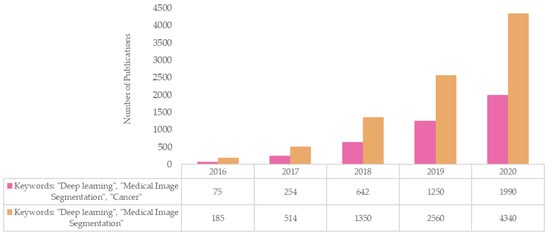
Diagnostics, Free Full-Text

Homework 2.pdf - 1/26/22 2:09 PM Homework 2 Homework 2 Code The
Electrical energy storage systems (EESSs) with high energy density and power density are essential for the effective miniaturization of future electronic devices. Among different EESSs available in the market, dielectric capacitors relying on swift electronic and ionic polarization-based mechanisms to store and deliver energy already demonstrate high power densities. However, different intrinsic and extrinsic contributions to energy dissipations prevent ceramic-based dielectric capacitors from reaching high recoverable energy density levels. Interestingly, relaxor ferroelectric-based dielectric capacitors, because of their low remnant polarization, show relatively high energy density and thus display great potential for applications requiring high energy density properties. In this study, some of the main strategies to improve the energy density properties of perovskite lead-free relaxor systems are reviewed, including (i) chemical modification at different crystallographic sites, (ii) chemical additives that do not target lattice sites, and (iii) novel processing approaches dedicated to bulk ceramics, thick and thin films, respectively. Recent advancements are summarized concerning the search for relaxor materials with superior energy density properties and the appropriate choice of both composition and processing routes to match various applications’ needs. Finally, future trends in computationally-aided materials design are presented.
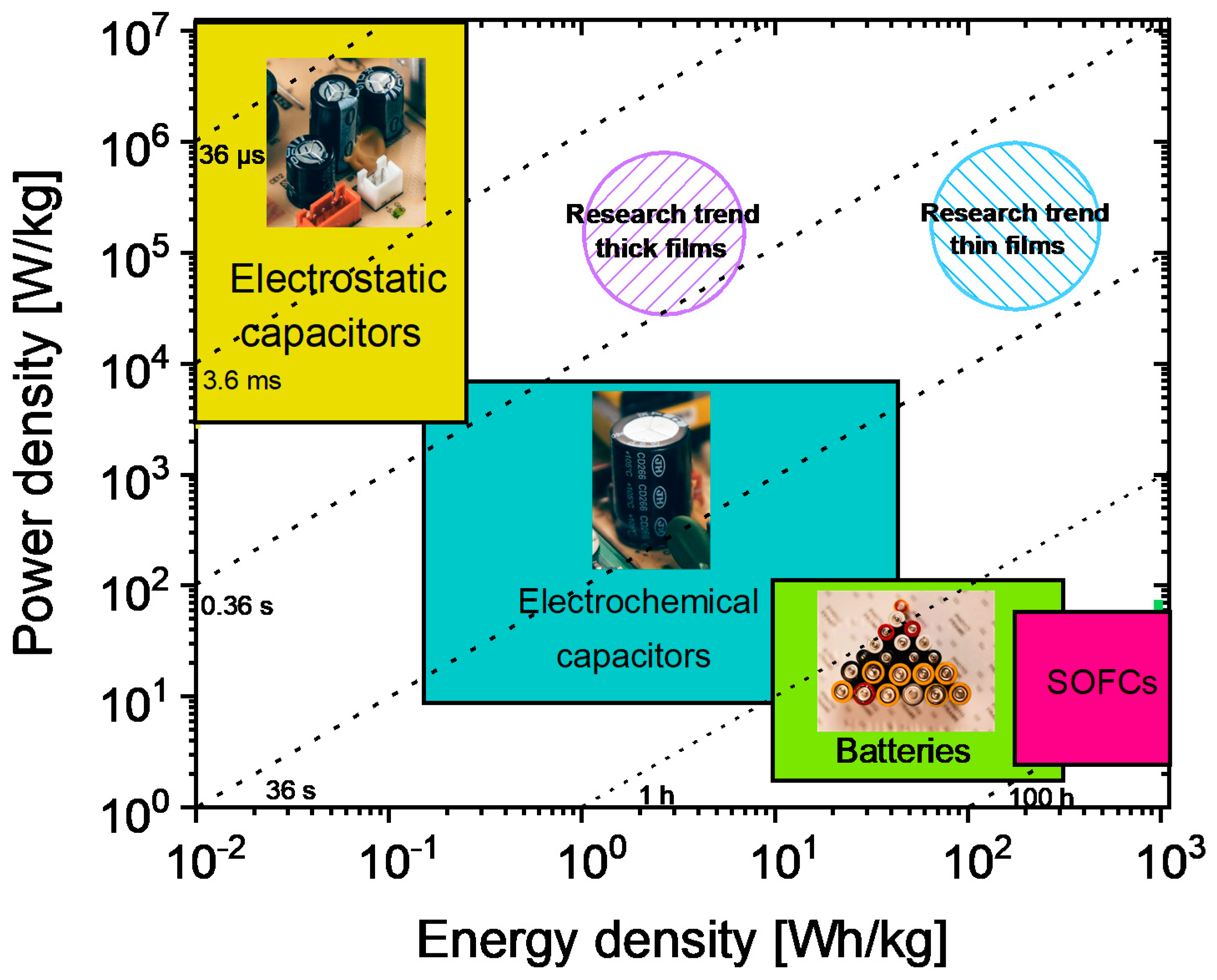
Materials, Free Full-Text
